Iodination of Aromatics with I2
Description: Treatment of an aromatic such as benzene with iodine (I2) and copper (II) chloride leads to formation of the iodinated benzene.
The rest of this page is available to MOC Members only.
To get access to this page, plus over 1500 quizzes, the Reaction Encyclopedia, Org 1 / Org 2 summary sheets, and flashcards, sign up here for only 30 cents/ day!
Real-Life Examples:
Org. Synth. 1956, 36, 46
DOI Link: 10.15227/orgsyn.036.0046
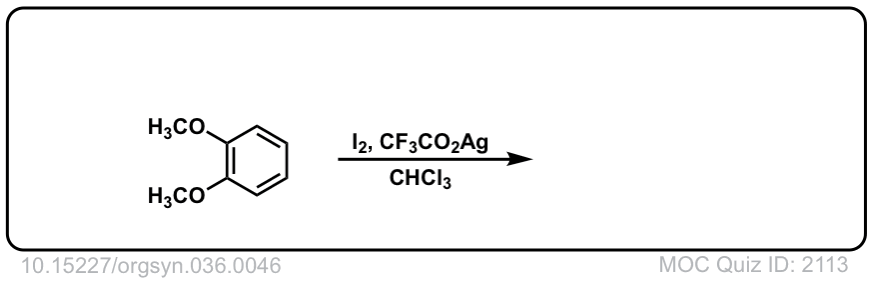 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
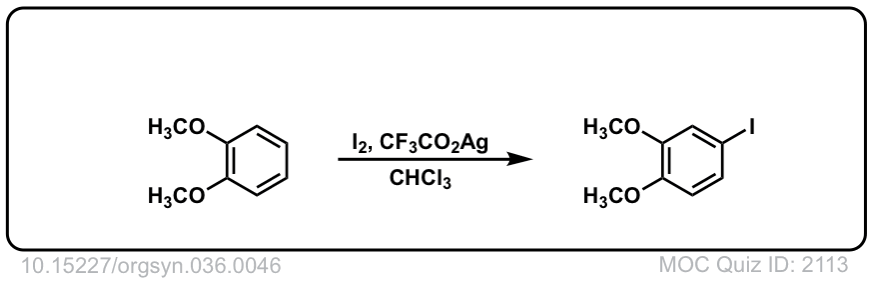
Check the description reaction, its CuI instead of CuCl2
Does reaction of molecular iodine with nitric acid not produce iodobenzene in greater yield? Lesser yield? Just as good?
Thanks!
but u forgetted that HI is reducing agent that can reverse the reaction toward the benzene ring
HI is not a reducing agent.
My text said that HI is a reducing agent.(That’s why direct Iodination fails to give Iodoalkane. Prescence of oxidising ahents like HgO is required to oxidise hydrogen iodide to iodine gas)